What is a Polar Molecule
Since electrons are more attracted to oxygen than hydrogen they tend to congregate on that end of the molecule. If the distribution looks even the molecule is nonpolar.
These two molecules do not form a solution as they cannot be mixed up.

. The electronegativity value for oxygen is 344 whereas the electronegativity value for hydrogen is 220. Water H 2 O is a molecule having a polar covalent bond. If they are highly different it can be said that the species is a highly polar molecule.
Examples of Molecules with Polar Covalent Bonds. Polar molecules also form when the spatial arrangement of chemical bonds leads to a more positive charge on one side of the. The difference in the distribution of electrons accounts for the best shape of the molecule.
Water has the capacity to break the detractions between the atoms in the molecule hence polar solids are soluble water. That gives the oxygen a negative charge and the hydrogens a positive charge creating a dipole. Polar Molecule Definition.
Learn more about its formation properties examples in this page. The division of a sample of a substance into progressively smaller parts produces no change in either its composition or its chemical properties until parts. What is the main application.
How does molecule shape change with different numbers of bonds and electron pairs. Molecule Polarity - PhET. A polar molecule is a chemical species in which the distribution of electrons between the covalently bonded atoms is not even.
Then compare the model to real molecules. Each oxygen-hydrogen bond is polar with the oxygen atom bearing the partial negative charge and the hydrogen atom the partial positive charge. Find out by adding single double or triple bonds and lone pairs to the central atom.
Polarity is a description of how different the electrical poles of a molecule are. Water is polar because it has a bent geometry that places the positively-charged hydrogen atoms on one side of the molecule and the negatively-charged oxygen atom on the other side of the molecule. Explore molecule shapes by building molecules in 3D.
Dipole-dipole forces are attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule. Oxygen is highly electronegative and pulls the electrons closely creating a partial negative charge. In this solution water is a polar molecule whereas oil behaves as a non-polar molecule.
Dipole-dipole forces have strengths that range from 5 kJ to 20 kJ per mole. The dipoles do not cancel out resulting in a net dipole. Molecule a group of two or more atoms that form the smallest identifiable unit into which a pure substance can be divided and still retain the composition and chemical properties of that substance.
The polarity of water and the corresponding hydrogen bonds create cohesion adhesion capillary action high specific. A polar molecule has a net dipole as a result of the opposing charges ie. Probably the thing you were interested in calculating is the dipole moment of a molecule which essentially involves summing the difference in negativities across atoms as vectors to get a dipole.
For example consider water and oil. They are much weaker than ionic or covalent bonds and have a significant effect only when the molecules involved are close together. The net effect is a partial dipole where the hydrogens have a partial positive charge and the oxygen atom has a partial negative charge.
In a solution a polar molecule cannot be mixed with the non-polar molecule. By contrast a polar molecule consists of lone pairs of electrons on a central atom and therefore has unequal sharing of electrons. Examples of Polar and Non-Polar Molecules A molecule may be polar or non.
If this is present then the molecule is polar. Because the molecule is angular rather than linear the bond dipole moments do not cancel and the molecule has a nonzero dipole moment. The atoms in a molecule have equal or nearly equal electronegativities and have zero or very small dipole moments.
Having partial positive and partial negative charges from polar bonds arranged asymmetrically. It has a permanent dipole moment which arises from differences in electronegativities between atoms. Water H 2 O is an example of a polar molecule since it has a slight positive charge on one side and a slight negative charge on the other.
Water - A Polar Molecule. Polar Covalent Bond is a bond that exists between two atoms consisting of electrons that are unevenly distributed. In contrast the water molecule is polar.
A polar molecule is a molecule containing polar bonds where the sum of all the bonds dipole moments is not zero. In this video Paul Andersen explains how the polarity of water makes life on the planet possible. Polar bonds form when there is a difference between the electronegativity values of the atoms participating in a bond.

Polar And Nonpolar Molecules Covalent Bonding Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Classroom

Polar Molecule Easy Science Molecules 10th Grade Science Chemistry

Chemistry Intermolecular Forces Polar Bonds And Polarity Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Classroom Physics Lessons

Why Is Water A Polar Molecule Molecules Polarity Of Water Covalent Bonding
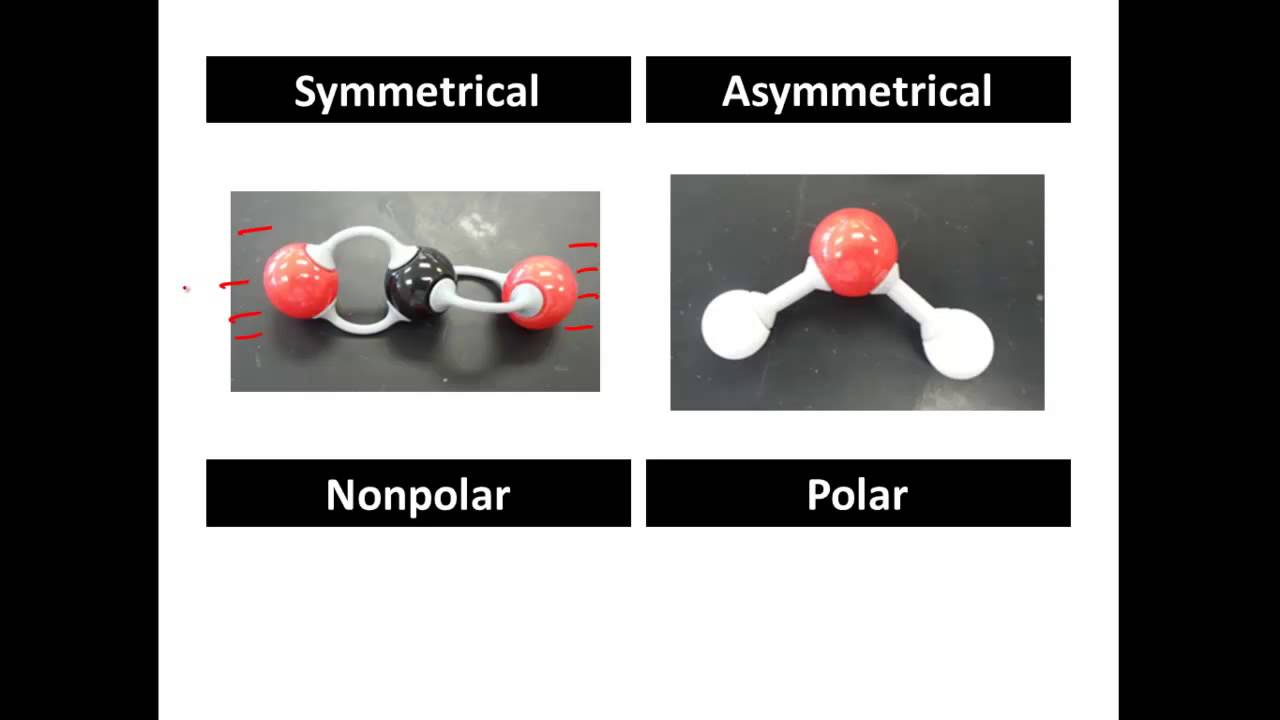
Polar And Non Polar Covalent Molecules Polar Vs Nonpolar Youtube Playlist Science Chemistry Science Activities Chemistry

What Is A Polar Molecule Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Classroom Chemistry Worksheets

0 Response to "What is a Polar Molecule"
Post a Comment